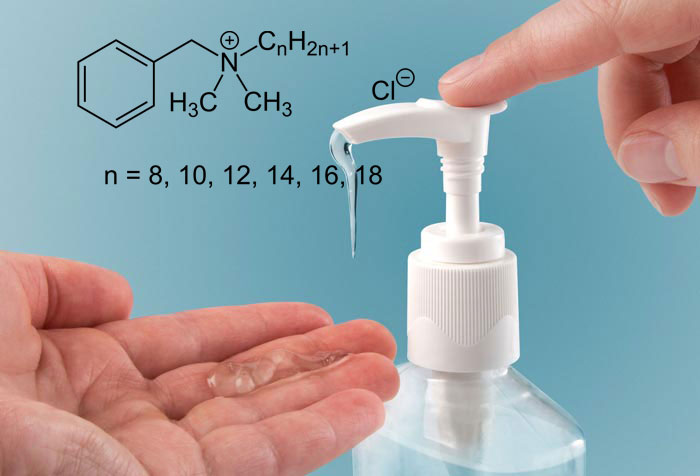
Benzalkonium Chloride
Benzalkonium chloride is a type of cationic surfactant that is considered a non-oxidative biocide. This biocide is based on quaternary ammonium compounds, which are effective even in low concentrations.
This biocide is soluble in water and is effective in preventing the activity of some vital bacterial enzymes (enzymes involved in glycolysis respiration), as well as releasing the contents of the bacteria into the environment. By increasing the contact time and concentration of the biocide, compounds containing nitrogen and phosphorus in the bacterial cell enter the surrounding environment, and thus the bacteria are destroyed. This material has the property of dispersing, spreading, and destroying sludge and algae.
Using this biocide may cause foaming. In order to make this biocide more effective, it is recommended to use it together with non-oxidizing isothiazolinone biocide.
This biocide can be used in all open or closed-circuit cooling and cooling systems, firefighting systems, ponds and pools, water transmission lines, etc.
Equipment and containers should be made of stainless steel, 316 steel, 304 steel, polypropylene, polyethylene, PVC, or Teflon.
Advantages of benzalkonium chloride
- It has a wide range of applications.
- The product is liquid and easy to use. (injection)
- It has a good spreading property, which means it is an effective dispersant.
- Its effectiveness in a different range of pH.
Benzalkonium chloride (BAC, BAK, BKC, BZK), known as alkylidene methyl benzyl ammonium chloride (ADBAC), is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. ADBACs are used in three main categories: as a biocide, cationic surfactant, and phase transfer agent. methylammonium.
Solubility and physical properties of benzalkonium chloride
Depending on the purity, benzalkonium chloride ranges from colorless to pale yellow (impure). Benzalkonium chloride is easily soluble in ethanol and acetone, but its solubility is slower in water. Its aqueous solutions should be neutral to slightly alkaline. Concentrated solutions have a bitter taste and a faint smell like almonds. Standard concentrates are produced as 50% and 80% by-weight solutions. A 50% solution is completely blue.
Other names of dimethyl benzalkonium chloride
Benzalkonium chlorides (BACs), also known as alkyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chlorides, quaternary alkyl dimethyl (phenylmethyl) ammonium chlorides, quartz disinfectants, BACs, benzalkonium chlorides, and QACs.
Properties of dimethyl benzalkonium chloride
Benzalkonium chlorides (BAC) due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Benzalkonium chloride is a broad-spectrum quaternary ammonium antibacterial agent. This material is cationically charged and creates an antibacterial effect by absorbing the negatively charged bacterial membrane.
Gram-positive bacteria are generally more sensitive than gram-negative bacteria. Its activity depends on the concentration of surfactant and also on the concentration of bacteria at the moment of injection. Activity is largely unaffected by pH but increases significantly at higher temperatures and longer exposure times.
Application of dimethyl benzalkonium chloride
It is widely used in medicine and pharmacy as a preservative in eye drops, in higher concentrations, it is also used as an antiseptic. This substance is a quaternary ammonium compound that acts as an antimicrobial agent by denaturing proteins and disrupting the cytoplasmic membrane.
It has also been used in various dental composites. Benzalkonium chloride is a key element in phase transition analysis, an important technology in the synthesis of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals. In cosmetic products, their antimicrobial properties are used to protect products from spoilage.
This substance is mostly used in personal care products such as powder creams, foot odor removers, face lotion, cleansers, cosmetics, and sunscreen. Also, this biocide or disinfectant is used in the food industry and many other industries:
- Egg disinfection before transfer to the hatchery
- In hatcheries for disinfection of hatcheries and disinfection of poultry halls, cages, and poultry equipment (drinkers, feeders, etc.)
- Disinfection of the place where animals are kept, maternity, calf breeding, and hospitals
- Disinfection of trucks transporting protein materials
- Disinfection of floors, boots and surfaces, and equipment in food factories
- Disinfection of entrance ponds for vehicles and livestock crossing in livestock and poultry farms and entrance ponds of poultry halls
Benzoalkonium chloride grades
If we want to categorize this material, we can see that it has both food grade and industrial grade. Its food-grade must be rinsed off the surface of the devices after consumption. In industrial grade, it is also different according to the type of use of rinsing. But it can be used in two levels based on its function:
- First grade as a preservative and antimicrobial
- Secondary as a surfactant
Mechanism of benzalkonium chloride
It works by killing microorganisms and preventing their growth, which is why it often appears as an ingredient in antibacterial wipes, antiseptic creams, and anti-itch ointments. The mechanism of action of bactericide, and microbicide is due to the disruption of intermolecular interactions.
This can cause the separation of the lipid bilayers of the cell membrane, which compromises the control of cell permeability and causes leakage of cell contents. Other biomolecular complexes inside the bacterial cell can also be degraded. Enzymes control a wide range of metabolic and respiratory cellular activities and are particularly sensitive to inactivation. Critical intermolecular interactions and tertiary structures in such highly specific biochemical systems can be easily disrupted by cationic surfactants.
Production of benzalkonium chloride
How is benzalkonium chloride made? By further adopting the synthesis of benzalkonium chloride, dimethyl-dodecyl amine hydrogen bromide is obtained after the synthesis of dodecanol, dodecyl bromide, then it reacts with the reaction of dimethylamine, finally, and benzyl chloride to obtain benzalkonium chloride.
Mechanism of action of benzalkonium chloride 20%
Benzalkonium chloride 20% by affecting the cell wall causes the coagulation of the cytoplasm and prevents the activity of some vital enzymes of microorganisms, and the chlorine ion in it causes the connection between DNA or RNA chains in viruses to be broken. To be Benzalkonium has a bactericidal effect even in low concentrations.
For more information regarding the purchase of Benzoaljonium chloride please contact our expert at Iran Petroleum.




Leave a Reply