Polymers in Medicine
The advantages of using polymer materials over other chemicals in the medical industry have made them one of the most used in this industry. In general, the use of polymers in medicine, in the manufacture of medical equipment, and also in medical implants are widely used today.
In this article, due to the wide range of applications of polymer materials in medical equipment and medical implants, we will continue to examine these materials in medical implants.
The consumables used in the body can be classified into metal materials, ceramic materials, polymer materials, and composite materials; among the materials used for biological purposes, polymer materials have a special place. Biomaterials are compounds of natural or synthetic origin that have various applications in the medical industry.
Biomaterials to replace tissue, restore tissue function with different methods, improve tissue function, correct and eliminate disorders, etc., are used in various ways, such as in suture thread, bone plates, replacement joints, heart valves, intraocular lenses, etc.
In the following, we first take a look at the characteristics of polymer biomaterials. In addition, since biomaterials are primarily used in orthopedic implants, in the rest of this article, we will examine their use in cases such as joint replacement, bone replacement, bone filler, joint connection, fracture repair, etc.
Properties of polymeric biomaterials
In terms of function in the body, polymeric biomaterials are divided into two categories. Polymers in medicine are bio-compatible, and they are also sustainable. The other category is biocompatible and biodegradable, which means they slowly break down in the body and disappear.
Biomaterials, whether biodegradable or non-biodegradable (stable), should have a series of physical-mechanical characteristics when they come into contact with body tissue or the living environment in general, depending on whether They use it.
The most important things polymers in medicine must have are tensile strength, bending strength, compressibility, impact ability, fatigue, creep, tearing, corrosion, abrasion, and cracking due to impact, as well as factors such as not being toxic or pathogenic. Immune reactions and blood clotting should not occur if the object is unstable in the body, the components resulting from its destruction should not be toxic or harmful, etc.
The most critical applications of Polymers in medicine in medical implants
- Bone filler using polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)
- Replacing joints using polyethylene (PE)
- Vertebral bone ossification using polyether ether ketone (PEEK)
- Artificial heart valves using polyurethane (PU)
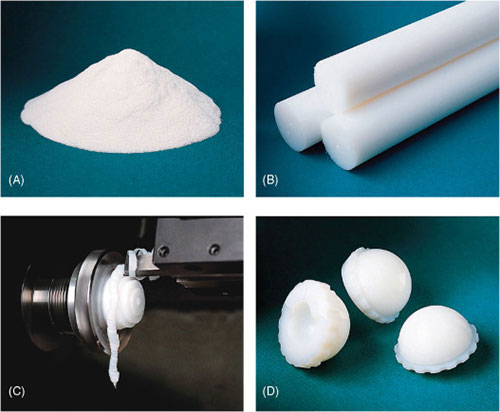
Bone filler using polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) – Polymers in Medicine
One of the groups of Polymers in medicine is Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) or bone cement consisting of a solid polymer powder and liquid monomer methyl methacrylate (MMA), along with a few other additives.
This mixture is doughy at first and becomes firm after a few minutes. PMMA has good resistance to unwanted chemical reactions and has good biocompatibility in the body in its pure state.
This material has a variety of uses; for example, these materials can be used in cases that have been damaged due to trauma or in the course of cancer; PMMA can be used to fill these empty spaces. Of course, there are also disadvantages, such as the toxicity of MMA, etc., which can be improved in some ways.
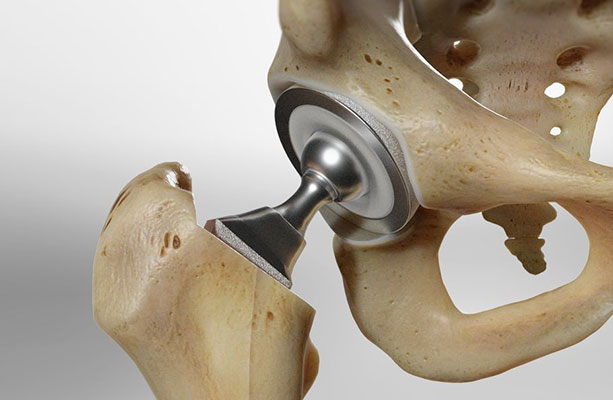
Replacing joints using polyethylene (PE) – Polymers in Medicine
One of the most widely used Polymers in medicine and in the field of orthopedic surgery is polyethylene, and they work well in replacement joints due to its properties. Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) or cross-linked polyethylene (HXPE) are used in replacement joints. One of the disadvantages of using them is that when wear occurs in the bone joint, the micron particles of UHMWPE are toxic and problematic.
Nowadays polymers in medicine, like meshed polyethylene is used to prepare a durable surface with low friction in the replacement of hip, knee, shoulder, and ankle joints. The cup part of the prosthesis is made of polyethylene, and the PMMA mesh is connected to the bone. The below figure shows two examples of total hip replacement by polyethylene.
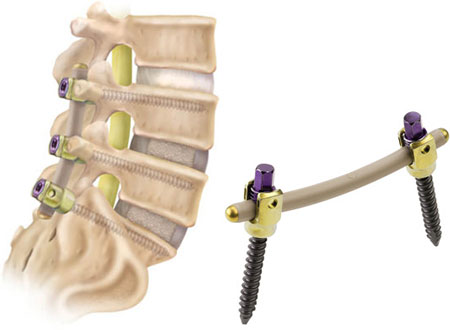
Vertebral bone ossification using polyether ether ketone (PEEK) – Polymers in Medicine
Another group of Polymers in medicine is PEEK. Polyether ether ketone has become a suitable choice for orthopedic implants due to its properties, such as high chemical resistance, biocompatibility, good mechanical properties, and stability against gamma radiation. Polyether ether ketone polymer has the same hardness as bone.
With higher relative flexibility, flexural modulus, and tensile strength than UHMWPE or PMMA, PEEK is one group of polymers in medicine that is used in some applications, such as the reconstruction of spine defects.
Artificial heart valves using polyurethane (PU) – Polymers in Medicine
Artificial heart valves are materials that are mainly used for patients who need a heart valve replacement. Polymers in medicine such as Artificial heart valves are divided into two main categories: mechanical valves and bioprosthetic valves.
Problems such as clogging on metal mechanical valves and low stability of bioprosthetic valves have turned attention towards the improvement of these materials. Polymers in medicine, such as polymer valves have been proposed as one of the promising materials in the construction of artificial heart valves. They are considered to solve the current problems of metal mechanical valves and bioprosthetic valves.
Biocompatibility, blood compatibility, and resistance to calcification and destruction are critical issues in polymer heart valves. Polyurethanes are one of the most popular materials due to their significant mechanical properties, hematopoiesis, and good hemodynamic behavior, which, despite problems such as calcification and degradation, are still the focus of many researchers in cardiovascular applications.
Conclusion
An implant is a type of medical device that is placed in a part of the body to replace a biological organ, support a damaged biological structure, or strengthen the structure. In this article, while introducing the use of polymers in medicine, we examined the characteristics of biomaterials. We also introduced four essential benefits of sustainable biomaterials in medicine.
For more information and advice in the petrochemical industry in medicine and medical equipment, please get in touch with our experts at Iran Petroleum.








Leave a Reply