Polypropylene – PP
Polypropylene, abbreviated as PP, is a thermoplastic composite polymer made from a combination of propylene monomers.
This product has different types and depending on its application, it is produced in different grades such as raffia, medical, etc. In the following text, the necessary information for the preparation of the product, as well as additional information about the production method, types, different applications, etc., are mentioned.
What is polypropylene?
Polypropylene is the second most widely used thermoplastic from the polyolefin family. PP is a versatile material that integrates properties such as lightness, strength, high heat resistance, rigidity, and flexibility. Polypropylene is molecularly a linear hydrocarbon resin whose chemical formula is C3H6.
Production and polymerization methods
Polypropylene is generally produced from propylene using the Ziegler-Natta polymerization method or metallocene catalysis. Polypropylene production starts from crude oil, where the crude oil is distilled and the naphtha cut is separated from it. Then naphtha is subjected to a cracking process, this process happens when naphtha is used as feed in petrochemical steam crackers.
Cracking converts naphtha into various olefins, including propylene. Then propylene is converted into polypropylene using the mentioned methods. The described items can be seen in the figure below:
Advantages of polypropylene
- Low density (0.9 – 0.91 g/cm3)
- Destructive resistance to environmental stress
- High tensile strength
- High rigidity
- Polypropylene is easily available and relatively cheap.
- PP has high bending due to its semi-crystalline nature.
- PP has a relatively slippery surface.
- PP is very resistant to moisture absorption.
- PP has good chemical resistance in a wide range of acids and bases.
- PP has good fatigue resistance.
- PP has good impact strength.
- PP is a good electrical insulator.
- Good mechanical strength
- Good molding properties
- Odorless and non-toxic
Disadvantages of polypropylene
- Polypropylene has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, which limits temperature applications.
- Sensitivity and damage to ultraviolet radiation.
- PP has less resistance to chlorine and aromatic solvents.
- PP is known to be difficult to paint because of its poor bonding properties.
- PP is highly flammable.
- Tendency to oxidize in the open air
Classification of PP based on the structure
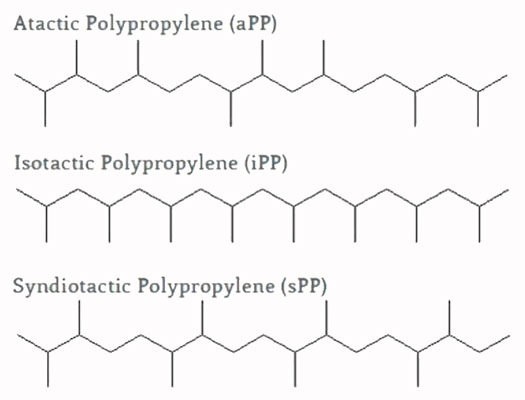
Based on the geometric order and location of molecules, different types of PP can be formed, which are isotactic, syndiotactic, and atactic.
Atactic (app)
- In this structure, methyl groups are randomly located on both sides of the main chain.
- This substructure has a low melting temperature and is a gummy substance that is used in the manufacture of some adhesives due to its high adhesive properties. Atactic polymer is an amorphous, flexible, and rigid material. In contrast to isotactic and syndiotactic polymers, polymers with high crystallinity are stiffer and less flexible. Industrial polypropylene is usually isotactic.
syndiotactic (spp)
- In this structure, methyl groups are placed one in the middle at the top and bottom of the main chain.
- This substructure has the same properties as the isotactic substructure, but they are more transparent due to less crystallinity. Also, it is more difficult to process than other grades. The highest crystallinity properties of these grades are respectively related to isotactic, syndiotactic, and atactic substructures.
isotactic (ipp)
- In this structure, methyl groups are located on one side of the main chain.
- The isotactic structure has a high melting temperature and is a crystalline and brittle material.
Types of polypropylene grades
Homopolymers and copolymers are the two main types of polypropylene available in the market; But there are other types of polypropylene, which we will mention below.
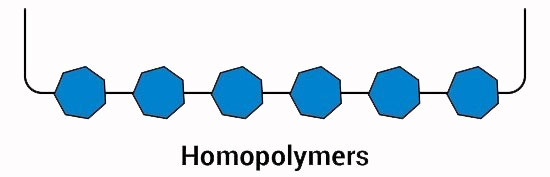
A. Homopolymers
Polypropylene is a homopolymer produced from the polymerization of propylene monomer alone. From the point of view of physical and mechanical properties, the difference between polypropylene homopolymer and copolymer is impact resistance, tensile strength, and hardness.
Even though PP homopolymer has higher tensile strength and hardness than PP copolymer, its main weakness is its impact resistance. In fact, polypropylene homopolymer is more fragile than polypropylene copolymer.
This weakness shows itself more at low temperatures, especially below zero. For this reason, the use of PP homopolymer in the production of injection parts that are exposed to impact and low temperature is extremely limited. To solve this weakness by adding ethylene monomer during propylene polymerization, PP copolymer has been produced.
Its main uses are:
- Packages
- Healthcare products
- Tubes
- Vehicles
- Electrical parts such as power cords
B. Copolymers
Polypropylene copolymer is produced from the polymerization of propylene with ethylene comonomer. PP copolymer has a higher impact resistance than PP homopolymer. By adjusting the amount of ethylene added to the polymer structure, adjusting the morphology of the copolymer, adjusting the type of crystallization, and also adjusting the molecular weight, the impact resistance can be adjusted and raised to a good extent.
Of course, it should be noted that increasing the impact resistance of polypropylene is done at the expense of reducing the hardness and stiffness of the polymer. Adding ethylene to the structure of PP during the polymerization of propylene reduces the structural order of polypropylene. Decreasing the structural order, in turn, causes a decrease in the amount of crystallization (crystallization) of PP. Due to the fragile structure of crystals, the reason for the increased impact resistance of PP copolymer compared to PP homopolymer is the decrease in crystallinity.
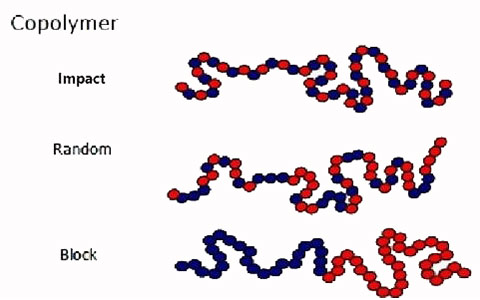
Copolymers are divided into three distinct categories:
1. Random Copolymer
In random copolymers, ethylene monomers are irregularly and separately located along the polymer chain. These polymers, usually containing 1-7% ethylene, are chosen where lower melting points, greater flexibility, and increased clarity are beneficial. They are flexible and optically transparent and are used for products that need a beautiful and excellent appearance.
2. Block Copolymer
In the block copolymer, the ethylene sections are located between the propylene sections along the polymer chain. By incorporating 5-15% ethylene, the impact resistance is greatly improved and extends below -20 degrees Celsius. Their stiffness can be increased by adding modifiers, traditionally elastomers, in a compounding process. Block copolymer is used in cases where high strength is required, such as industrial applications.
3. Impact Copolymer
This type of polypropylene has 45-65% ethylene and it is used in parts that need impact resistance, such as packaging, household appliances, and in various parts of cars and electrical appliances.
C. Expanded Polypropylene
This type of polypropylene has the following characteristics:
- Very low density
- High strength
- Impact resistant
- Insulation
Expanded propylene is used in many cases; From cars, and construction products to consumer goods and more.
D. Terpolymer
Terpolymers are formed by ethylene and butane monomers. Their features are:
- Compared to other types of polypropylene, they are more transparent.
- They reduce the composition of monocrystalline comonomers in polymers.
E. High Melt Strength Polypropylene
The characteristics of this polypropylene are:
- Long chain branched polymer
- It has a high melting point
- The ability to expand in the molten phase
- High chemical resistance
High melting point polypropylene is widely used in:
- Production of soft foams with low density
- food packing
- Automotive industry
- construction industry
Polypropylene applications
- Injection Molding
PP is the most widely used in this category, which is used in the production of electrical and electronic devices, caps and hats, toys, luggage, household items, and packaging and automobile industries.
- Fibers
The second application of PP in this category is in the production of fibers used behind carpets, as a substitute for fibers and hemp in carpets and sack yarns, non-woven fibers, and fabric for heat and cold insulation clothes.
- Sheet/Film
This part of PP application has grown significantly in recent years. Candy and chocolate packaging industries, cigarettes, graphic films and printing, food packaging sheets that are formed by heat.
- Blow Molding
This grade is mostly used in the production of tanks, bottles, and cans.
- Pipe
All kinds of sewage pipes and pipes and all kinds of wires and cables are products of this group of PP.
- Extrusion Coating
This part of PP consumption is gradually replacing the use of LDPE light polyethylene. polypropylene is one of the plastics that have various applications in different parts and also as fibers. Their higher melting point and service temperature compared to other polymers has led to the increasing development of their use in various parts. On the other hand, due to their acceptable strength and low water absorption, their fibers can compete with nylon fibers in many applications, such as for carpeting around swimming pools or miniature golf courses.
Contact our professional experts at Iran Petroleum for price information and advice on choosing the right polypropylene (PP) for you.






Leave a Reply