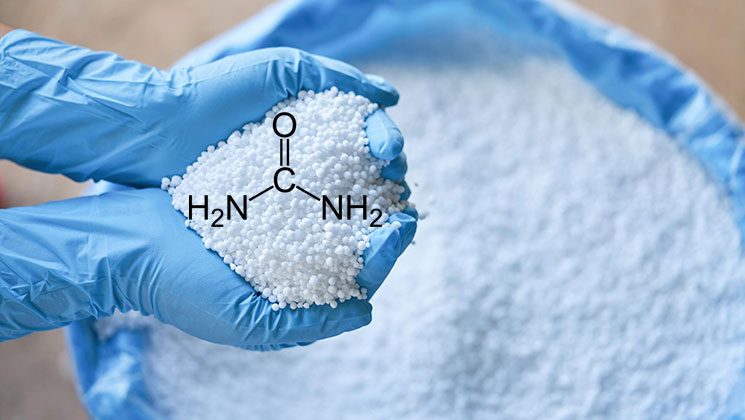
Urea
The world’s most widely used solid nitrogen fertilizer is urea CO(NH2)2. Animal urine also contains urea, which is commonly found in nature. This material is efficient for transferring to farms and applying to fields because of its high N content.
The method of production of Urea
In order to produce urea fertilizer, ammonia gas (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are combined at elevated temperatures and pressures. By using specialized granulation equipment, molten urea is formed into spheres or hardened into a solid prill by falling from a tower. Biuret can be harmful when sprayed on plant foliage when two urea molecules combine during urea production. Due to carefully controlled conditions during manufacturing, most commercial urea fertilizers contain only low levels of biuret. In some cases, though, the chemical with lower biuret content can be used for special purposes. NH3 is the main input for urea production, so the material manufacturing plants are generally located near NH3 production facilities. There are several methods for transporting this material around the world, including ocean vessels, barges, rails, and trucks.
The application of Urea in different industries
1. Agriculture
It is estimated that more than 90 percent of global urea production is destined for use as a nitrogen-releasing fertilizer. The nitrogen content of urea is the highest among all solid nitrogenous fertilizers in common use (46.7%). As a result, it is the nitrogen nutrient with the lowest transportation costs.
When it is hydrolyzed in the soil, it returns to ammonia and carbon dioxide. Plants are able to absorb nitrate from the soil when ammonia is oxidized by bacteria. There are also many formulations of solid fertilizers that contain the chemical. In combination with ammonium nitrate, the chemical is extremely soluble in water, making it an ideal fertilizer for use in fertilizer solutions (e.g., foliar feed). Due to their narrow particle size distribution, granules are preferred for the application of fertilizers.
Biuret is the most common impurity that occurs in synthetic urea, and its presence must be less than 2 percent of the time to prevent the growth of plants.
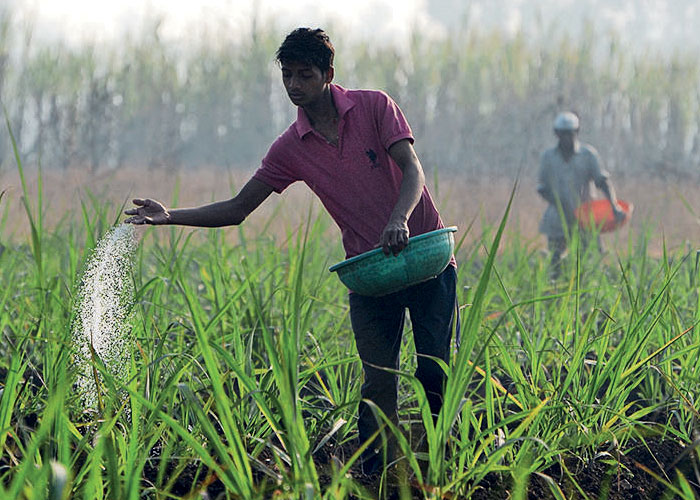
The amount of urea spread in farm
The amount of urea spread will vary depending on the type of farm and region, but the actual rate of spread will be between 40 and 300 kg/ha. To minimize leaching losses and increase the efficiency of nitrogen use, it is better to apply several small to medium applications at intervals rather than one heavy application. To reduce loss of nitrogen from volatilization (the process of converting nitrogen into ammonia gas in the atmosphere),the chemical should be spread prior to or during rain during the summer. The use of this material in combination with other fertilizers may result in problems of physical quality.
A uniform distribution of urea is essential due to its high nitrogen content. Calibration and proper use of the application equipment are essential. Drilling must not occur on contact with or close to seeding due to the possibility of germination damage. This chemical is dissolved in water and can be sprayed or applied through irrigation systems.
The amount of this material to be dissolved in 100 liters of water should not exceed 30 kg when preparing urea solutions for fertigation (injection into irrigation lines).
For horticultural crops, urea concentrations of 0.5 to 2.0 percent are often used in foliar sprays. It is important to seek advice before using urea sprays, as they may damage crop foliage. When applying urea sprays regularly to sensitive horticultural crops, low-biuret grades of urea should also be used.
The atmosphere absorbs moisture from urea, just like most nitrogen products. Consequently, it should be stored on pallets in sealed bags or undercover with a tarpaulin if stored in bulk. A cool, dry, well-ventilated area is also recommended for storing solid fertilizers.
2. Uses in the chemical industry
Many important chemicals are manufactured from the chemical. In particular, urea-formaldehyde resins are used in various plastics Marine plywood uses adhesives such as urea-formaldehyde or urea-melamine-formaldehyde. Other industrial feedstocks include potassium cyanate explosive urea nitrate.
Clathrates formed by urea can trap many organic compounds. Interpenetrating urea molecules form channels to hold organic compounds. Separating mixtures using this behavior has been used to produce aviation fuel, lubricating oils, and separate paraffin.
Molecular handedness must be the same in all helices in a crystal due to interconnections. During nucleation, this can be determined by seeding the crystal. Racemic mixtures have been separated using the resulting crystals.
3. Urea in automobile systems
The NOx pollutants in exhaust gases from combustion are reduced by using this material in SNCR and SCR reactions, for example, in power plants and diesel engines. Injecting this material into the exhaust system is part of the Blue Tec system, for example. Catalytic converters convert ammonia produced by urea decomposition into nitrogen and water after reacting with nitrogen oxide emissions.
4. Uses of this material in laboratories
The non-covalent bonds in proteins are disrupted by urea at concentrations up to 10 M. It is possible to take advantage of this property in order to increase the solubility of some proteins. Deep eutectic solvents, or ionic liquids, are made from this material and choline chloride.
Fuel cells can generate electricity from this chemical as a hydrogen source. When this chemical is electrolyzed from urine or wastewater, hydrogen can be produced at a lower voltage and use less energy than when water is electrolyzed. However, bacteria normally rapidly degrade urea.
5. Medical usage
A topical dermatological product that contains urea promotes rehydration of the skin. Non-surgical nail debridement can also be achieved using 40 percent urea preparations covered by an occlusive dressing. Earwax can also be removed with this drug.
Injections of this chemical are used for abortions just like saline injections. Also known as urine therapy, it is a form of alternative medicine.
Urea nitrogen in the blood is measured by the blood urea nitrogen test (BUN). The test measures the function of the kidneys.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), which causes ulcers in humans, is detected using urea breath tests labeled with carbon-14 or carbon-13. An enzyme called urease is detected in the test, which is produced by Helicobacter as a byproduct of urea produced by the bacteria. As a result, the stomach environment surrounding bacteria is less acidic (pH is increased). Species of bacteria that are similar to H. pseudo pylori can also be detected in apes, dogs, and cats (including big cats).
6. The de-icer
The use of this chemical as a de-icing agent is a safe and non-corrosive option. On runways, walkways, landing gears, and other vehicles’ undercarriages that should always be protected from corrosion, the chemical can be used easily. De-icing operations at many airports are conducted with urea rather than highly corrosive chloride salts.
7. Other commercial uses
- Nitrocellulose explosives require this stabilizer
- Nitrogen provides growth stimulation at a relatively low cost as part of animal feed
- Resurfacing snowboarding half pipes and terrain parks with a non-corrosive alternative to rock salt
- Additive to cigarettes that enhances their flavor
- Nair or Veet hair removal products use this ingredient as their main ingredient
- In pretzels produced in factories, it acts as a browning agent
- Hair conditioners, facial cleansers, bath oils, and lotions may contain this ingredient
- It creates an endothermic reaction when mixed with water in some ready-to-use cold compresses for first-aid use
- With other salts, it acts as a cloud-seeding agent
- The urea-potassium bicarbonate mixture is a common flame-resistant charge in dry chemical fire extinguishers.
- Tooth-whitening products often contain this ingredient
- Dish soap’s main ingredient
- Fermentation of sugars into ethanol requires ammonium phosphate, as a yeast nutrient
- Plankton use the material as a source of nutrition for geoengineering experiments
- Hide glue can be extended in both working temperature and open time by adding this additive
- For textile dye baths or printing, as a solubility enhancer and moisture retainer
Iran is one of the leading countries in the production and exporting of Urea
According to Trade Data Monitor (TDM), Iran’s urea exports increased 26% year-over-year to nearly 4.2m tons in 2018, despite US sanctions.
US sanctions, which were imposed on 6 August 2018 and became effective on 4 November 2018, had a limited impact on the increase due to higher production in the country and an initial limited impact of US sanctions.
With 1.9 million tons exported in 2018, Iranian urea was mostly headed for India, followed by Turkey at nearly 400,000 tons. The chemical was also exported to China in over 800,000 tons.
The production of Iran’s urea fertilizer has grown by 7% annually since 2014. Among other countries, the country produced 5,580,540 metric tons of the chemical in 2019. The United States has overtaken Iran for the fifth position, with 5,703,251.53 Metric Tons, while Canada is in fourth place with 4,056,762 Metric Tons. The largest producer was India with 24,282,045.33 Metric Tons in 2019, a 1.6% increase over 2018. According to this ranking, Russia, Indonesia, and Pakistan are ranked 2, 3, and 4 respectively. At +57% per year, Nigeria had the best growth rate, while Morocco had the worst growth rate at -59.4% per year.
If you want to order this chemical from Iran, please do not hesitate to send Iran Petroleum an email.








Leave a Reply